Hair fungus, also known as scalp fungus or tinea capitis, is a common fungal infection that affects the scalp and hair follicles. It is primarily caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm and humid environments. These fungi can invade the hair shaft, causing various symptoms and scalp issues.
The most common types of fungi that cause hair fungus include Trichophyton and Microsporum. These fungi can be transmitted from person to person through direct contact with an infected individual, sharing contaminated objects like combs, brushes, or hats, or by coming into contact with fungal spores present in the environment.
Symptoms of hair fungus can vary, but they often include:
Itchy scalp: Infected individuals may experience persistent itching on the scalp, which can be quite uncomfortable.
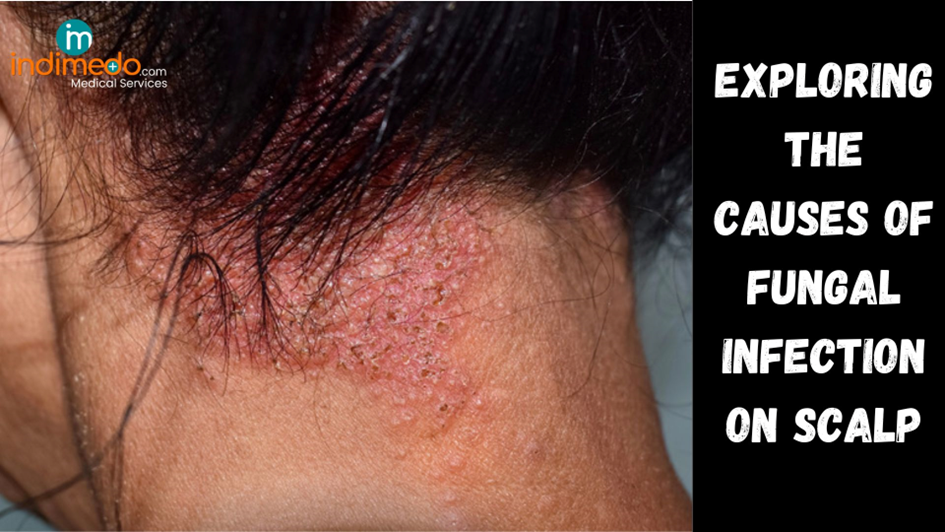
Redness and inflammation: The affected area of the scalp may appear red, inflamed, and irritated.
Scaling and flaking: The scalp may develop scales and flakes, similar to dandruff, which can be visible on the hair and clothing.
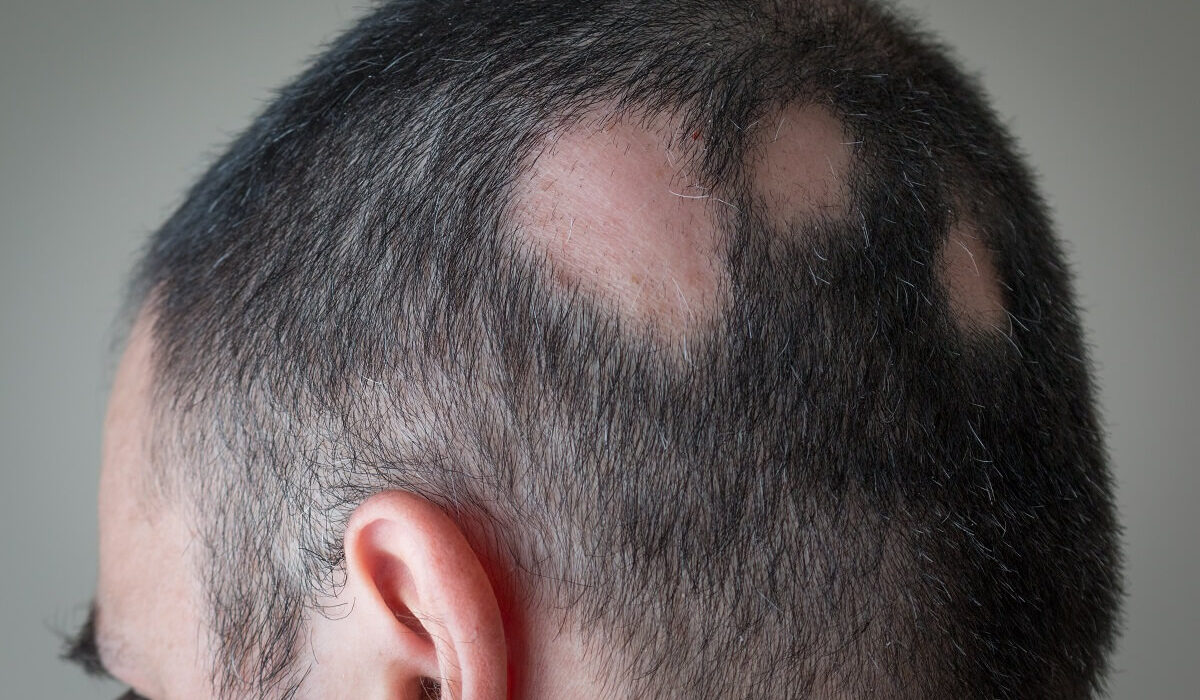
Hair loss: Fungal infections can cause hair to become weak and brittle, leading to hair breakage and eventual hair loss.
Patches and bald spots: In some cases, circular patches of hair loss may occur, leaving bald spots on the scalp.
If left untreated, hair fungus can spread to other parts of the body or to other individuals. It is particularly common in children, but it can affect people of all ages.
Treatment for hair fungus typically involves antifungal medications, either in the form of topical creams, shampoos, or oral medications. In severe cases, oral antifungal medications are usually prescribed to eradicate the infection. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as regularly washing hair and avoiding sharing personal items, can help prevent the spread of hair fungus. If you suspect you have hair fungus, it is best to consult a healthcare professional or a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.